Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis with secondary Aspergillus infection: A case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17532/jhsci.2021.1366Keywords:
Fungal infection, milky appearance bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, whole lung lavageAbstract
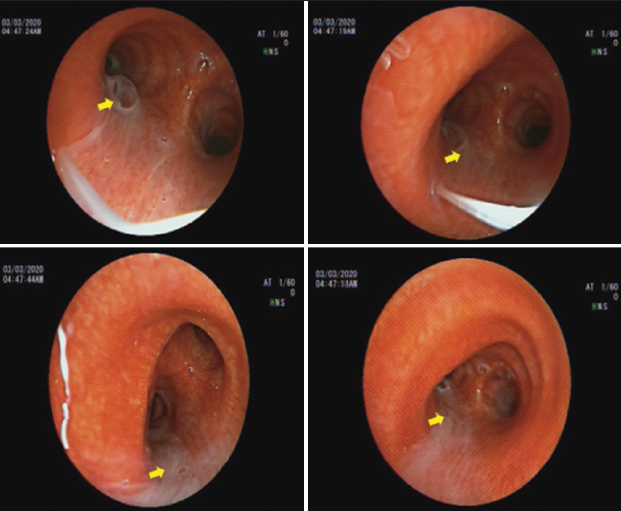
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare disease with mostly due to autoimmune toward granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. In some conditions, PAP followed with secondary infection. A 34-year-old woman came with progressive shortness of breath, chronic dry cough, and mild fever. The chest High-Resolution Computed Tomography showed ground-glass opacity with septal reticulation or known as the crazy-paving pattern, and a cavity on the upper lobe of the left lung. The patient underwent bronchoscopy for diagnostic and therapeutic measures and found milky appearance bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). The serum galactomannan came out positive. Fungal infection detected from the BALF culture, Aspergillus fumigatus, hence fulfilling the diagnosis of PAP with probable invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The patient showed clinical improvement after undergoing whole lung lavage and given anti-fungal medications.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Fanny Fachrucha, Sita Andarini, Mia Elhidsi, Rizky Yudha Irawan, Romi Beginta, Dianiati Kusumo Sutoyo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










