The role of Kinesio taping in enhancing functional performance among patients with musculoskeletal impairments
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17532/jhsci.2025.2955Keywords:
Kinesio taping, musculoskeletal disorders, upper extremity, functional recovery, physiotherapyAbstract
Introduction: Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are among the leading causes of disability worldwide, often resulting in pain, loss of function, and reduced quality of life. Kinesio Taping (KT) has been proposed as a supportive, noninvasive technique to enhance rehabilitation outcomes by improving neuromuscular activation, proprioception, and circulation. This research aims to evaluate the effect of KT on upper-limb functional improvement in patients with MSDs undergoing standard physiotherapy.
Methods: This prospective interventional study included 57 participants divided into a control group receiving conventional physiotherapy and an experimental group receiving additional KT. Functional status was assessed using the Upper Extremity Functional Index (UEFI) at 3 time points: before therapy, mid-treatment, and after therapy. Statistical analyses included the Mann–Whitney U test, Kruskal–Wallis test, and multiple linear regression.
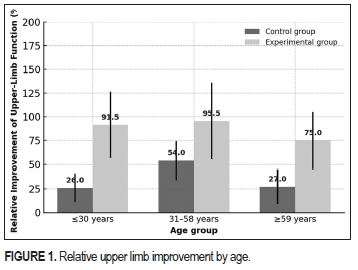
Results: At baseline, the KT group had significantly lower functional scores (median 24.0, Interquartile Range [IQR] 19.0–27.0) than controls (median 35.0, IQR 25.0–47.0; p = 0.02). During treatment, both groups improved, but the KT group demonstrated faster functional recovery (p = 0.033). At completion, both groups achieved similar UEFI scores; however, the total functional gain was nearly twice as high in the KT group (21.5 vs. 12.5 points). Relative improvement reached 90% in the KT group compared with 36% in controls. Regression analysis confirmed that KT application was a significant predictor of upper-limb functional improvement (β = 0.552, p = 0.002).
Conclusion: KT significantly accelerates upper-limb functional recovery and enhances rehabilitation outcomes when used as an adjunct to physiotherapy. Its simplicity, safety, and cost-effectiveness make it a valuable addition to standard musculoskeletal rehabilitation.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dinko Remić, Bakir Katana, Amra Mačak Hadžiomerović, Eldad Kaljić, Dženan Pleho, Amila Kapetanović, Lejla Hadžić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










