Effectiveness of intradialytic muscle stretching exercise onmuscle cramps among patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis in Oman - A randomized controlled trial
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17532/jhsci.2025.2777Keywords:
Effectiveness, intradialytic muscle stretching exercise, muscle cramps, maintenance hemodialysis, OmanAbstract
Introduction: Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) typically exhibit symptoms of the “uremic” syndrome and lower quality of life. Intradialytic muscle stretching exercise has been proposed as a method to improve activity levels by reducing uremic symptoms. In Oman, hypertension and diabetes increase the risk of ESRD, the sixth leading cause of death. ESRD patients in Oman require more dialysis, straining healthcare financial burden.
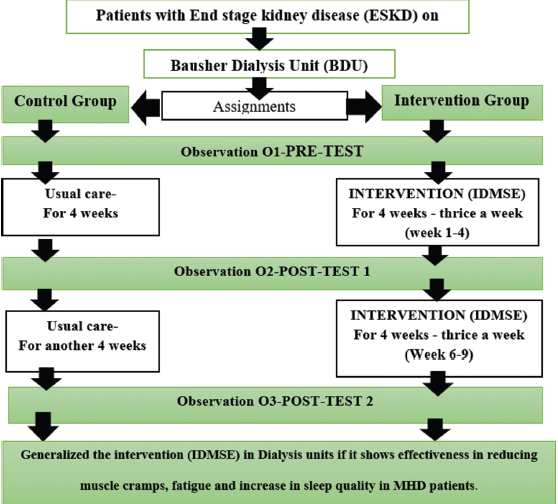
Methods: A pre- and post-test randomized controlled trial was conducted at the tertiary hospital in Oman, involving 78 individuals (n1 = 39 and n2 = 39). The study included demographic data and a muscle cramp questionnaire chart.
Results: In the third observation, the intervention group experienced less pain in hour III (p = 0.012) and hour IV muscle cramps (p = 0.004). Heart disease was associated with 2nd-h muscle cramps (p = 0.032). Prior cramp episodes were significant, whereas 2nd-h cramp patterns were not (p = 0.079). The timing of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th-h muscle cramps was associated (p = 0.006, p = 0.02, p = 0.01). Coping evaluations in the 3rd and 4th h were associated (p = 0.003, p = 0.313).
Conclusion: Intradialytic stretching exercise may serve as a non-pharmacological treatment for maintenance hemodialysis patients. This low-risk, cost-effective method has the potential to improve patient care, reduce symptoms, hospitalization rates, and enhance physical and mental performance.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Iman Al Rahbi, Eilean Rathinasamy Lazarus, Omar AlZaabi, Huda Al-Noumani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










