Application of rapid antigen tests in the prevention of the transmission of SARS-COV-2 in a hospital setting
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17532/jhsci.2022.1618Keywords:
Rapid antigen tests, COVID19, prevention, transmission, hospitalAbstract
Introduction: The pandemic of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) presented a major challenge to health-care systems around the world. To ensure the continuity of hospital care for patients with cardiovascular diseases, the clinic has formulated the strategy for prevention of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 across the hospital environment. The purpose of this paper is to present the strategy for the prevention of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in a healthcare facility, using Antigen Rapid Diagnostic Tests (Ag-RDTs).
Methods: A description of the work from the hospital committee for the prevention and control of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic is presented. The hospital has adopted the zero-case strategy. Each positive Ag-RDTs test was sent for confirmation by real-time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR).
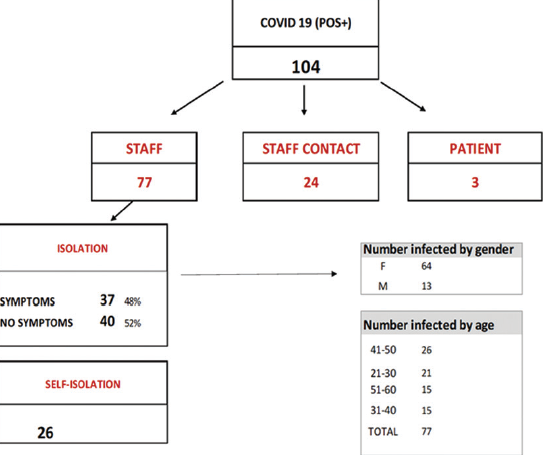
Results: During the observed period, 6569 tests were performed at the Magdalena Clinic. Of these, a total of 6100 Ag-RDTs were performed, while 469 were recorded by RT-PCR test. Of these tests, a total of 181 tests showed a positive result, which is a share of 2.75% of all tests performed, of which 144 (2.19%) positive findings were detected among staff. In Ag-RDTs alone, a total of 86 positive people were detected, which is 1.41% of those tested on this type of test.
Conclusion: The use of antigen rapid diagnostic tests is an effective and reliable method for the early detection of asymptomatic individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 in a hospital setting. This strategy can significantly contribute to the insurance of uninterrupted healthcare, providing regular workflow processes, and the care of patients in the safest possible way.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Dijana Babić, Branko Kolarić, Maša Šams Bival, Mihajlo Šesto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










